Consent Authorization
During the consent authorization process, the banks redirect customers to provide consent for TPPs to access their banking information. The process is as follows:
- TPP requests to access the banking information of a customer.
- Bank validates the TPP’s request.
- The bank redirects the requested information (containing the information the TPP application wants to access) to the customer.
-
The bank authenticates the customer. See below for the default login page of the consent page:
-
A list of bank accounts and the information that the TPP wishes to access are displayed.
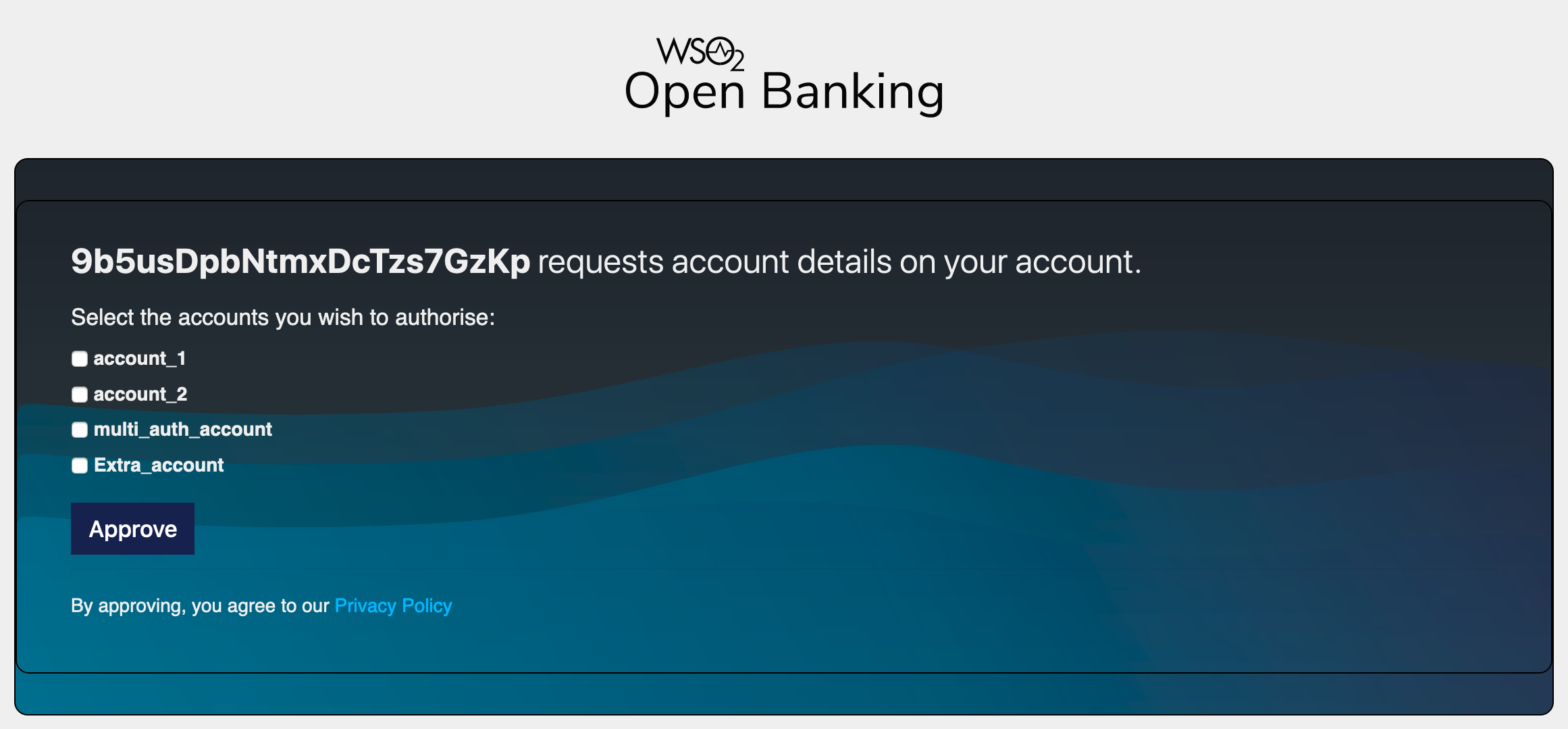
-
The customer can view the information before consenting or denying it. For example,
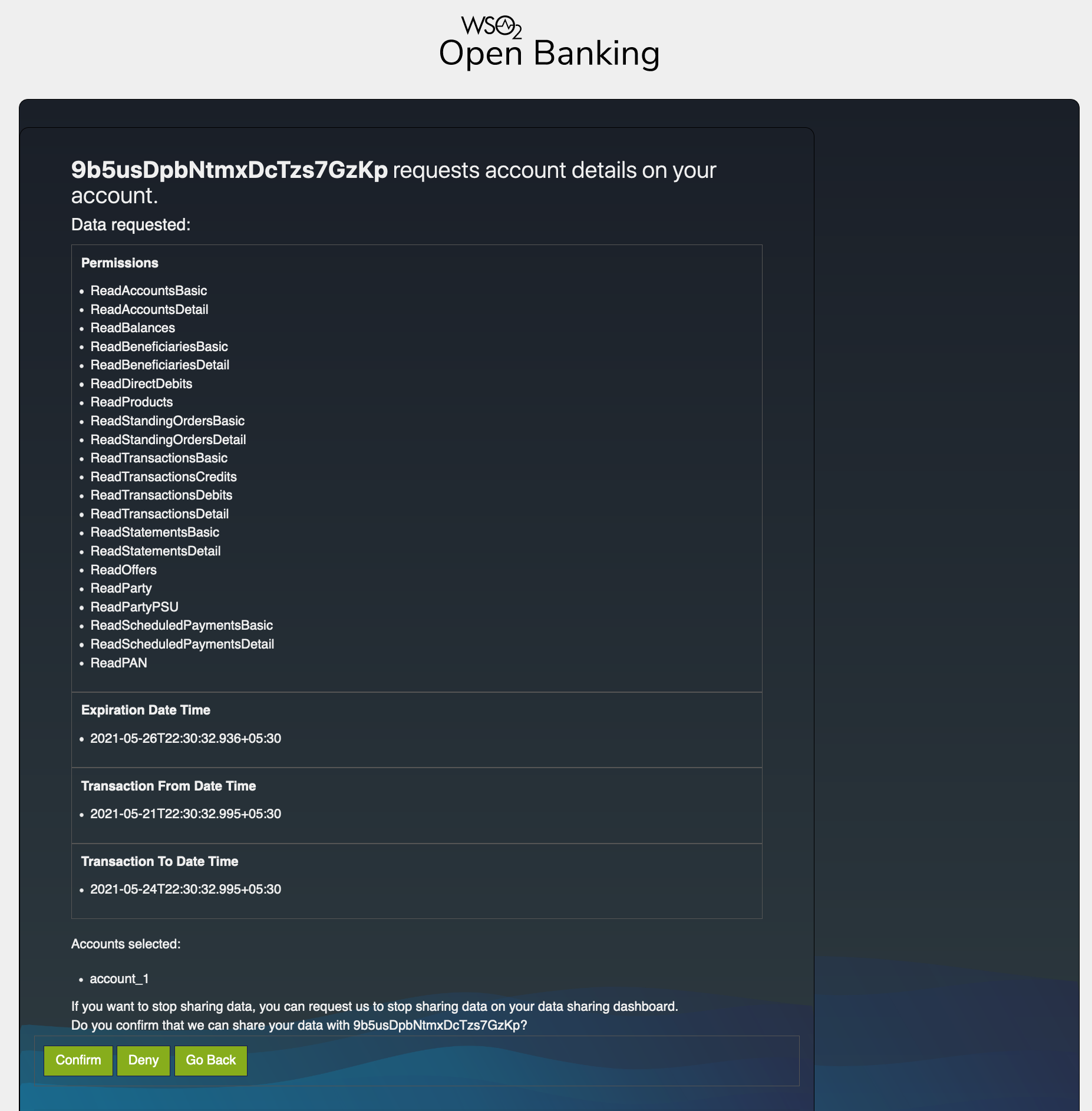
Consent Authorization in WSO2 Open Banking¶
Following components perform the consent authorization:
Authorization endpoint¶
Before the TPP application accesses the customer's banking information, the TPP sends an authorization request to get the customer's consent for it. The authorization request contains a request object. This request object is a self-contained JWT, which helps banks to validate the TPP.
The method of sending the authorization request can vary as follows:
- Send the authorization details in the authorization URL
The TPPs share the request object containing the authorization details to the authorization server and obtain the authorization URL.
- Send the authorization details as a reference in the authorization URL
The TPPs push authorization details directly to the authorization server and obtain a reference. This method is also
known as Pushed Authorization. The reference is notated by the claim; request_uri. Thereby, it prevents:
- Intruders from intercepting the authorization information sent in the request_object
- Authorization request calls becoming bulky with the authorization details signed in the JWT
and protects the confidentiality and integrity of the authorization details when passing through a TPP application.
Pushed Authorization web application¶
The TPPs obtain request_uri which is a reference to the authentication and authorization details sent in the
pushed authorization request.
- Pushed Authorization - /par endpoint
Upon successful invocation of the /par endpoint, TPPs will receive a request_uri value with an expiration time. Therefore, the reference is only valid until the expiration time for the subsequent authorization invocation.
Given below is a successful response:
{
"request_uri": "urn:ietf:params:oauth:request_uri:bwc4JK-ESC0w8acc191e-Y1LTC2",
"expires_in": 60
}This same request_uri value is used in the subsequent authorization request as well.
Click here to see configurations related to the Pushed Authorization web application...
- Open the
<IS_HOME>/repository/conf/deployment.tomlfile. - Add the following configurations that allow you to change the format and the expiration time of the
request_urireference:
[open_banking.push_authorisation]
expiry_time=60
request_uri_sub_string="substring"Note
You can change the format of the request_uri using the request_uri_sub_string tag.
{
"request_uri": "urn:<substring>:bwc4JK-ESC0w8acc191e-Y1LTC2",
"expires_in": 60
}Authorization web application¶
The TPPs obtain an authorization URL that redirects the customer to a web interface hosted by the bank. In this web application, the customer:
- Logs in using the login credentials.
- Views information that the TPP requested to access.
- Selects the accounts that the TPP can access.
- Provides consent to the TPP to access the information.